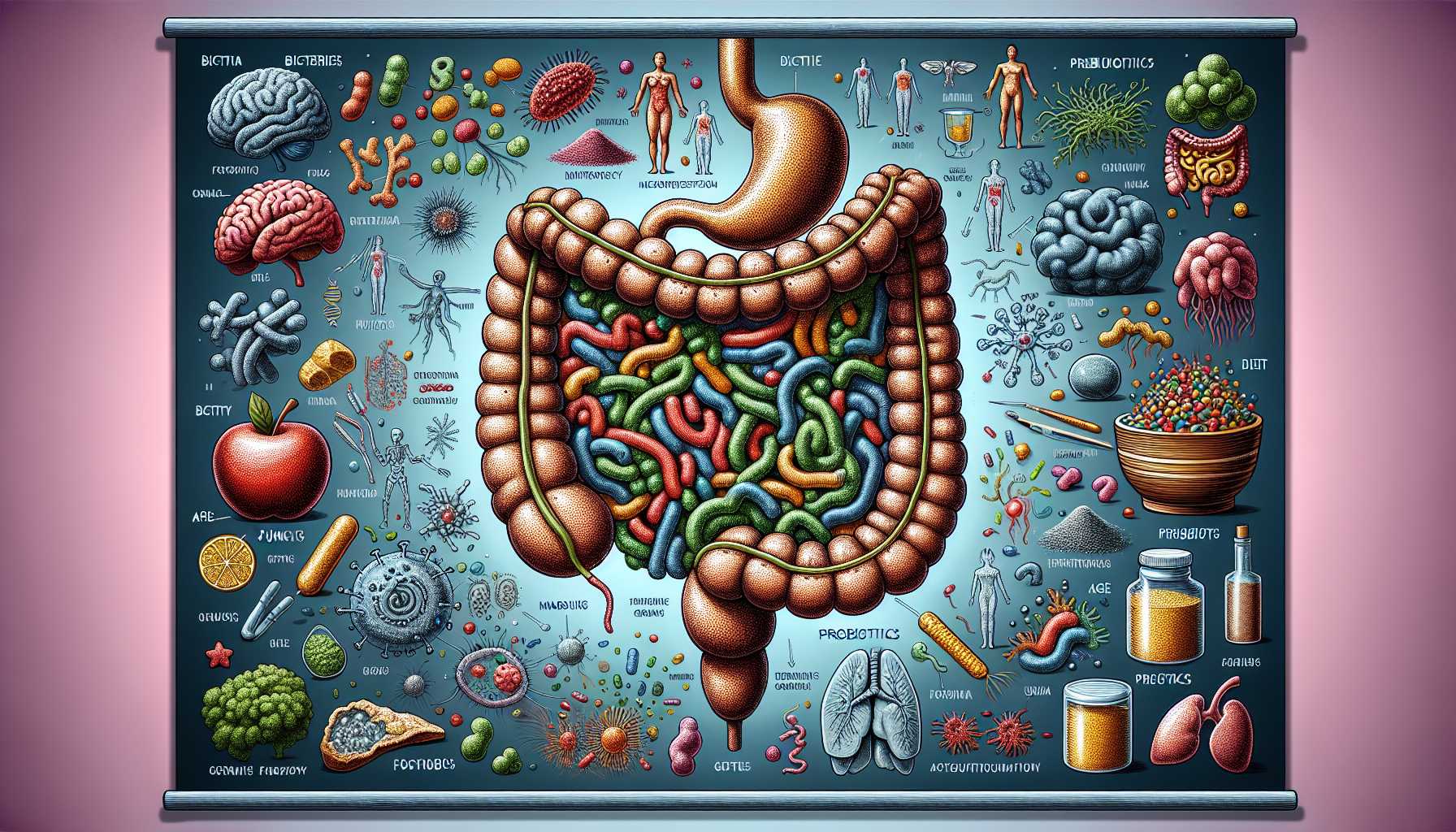
Understanding the Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Health
The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract.
Mikrobiom jelitowy odnosi się do bilionów mikroorganizmów, w tym bakterii, wirusów, grzybów i innych mikrobesów, które zamieszkują przewód pokarmowy.
These microbes play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall health by influencing metabolism, immune function, and even mental health.
Te mikroby odgrywają kluczową rolę w trawieniu, wchłanianiu składników odżywczych i ogólnym zdrowiu, wpływając na metabolizm, funkcję immunologiczną, a nawet zdrowie psychiczne.
The composition of the gut microbiome varies among individuals and can be affected by factors such as diet, age, genetics, lifestyle, and the use of antibiotics.
Skład mikrobiomu jelitowego różni się wśród pojedynczych osób i może być wpływany przez takie czynniki, jak dieta, wiek, genotyp, styl życia i stosowanie antybiotyków.
A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is essential for maintaining good health, while an imbalance, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders, obesity, and autoimmune diseases.
Różnorodny i zrównoważony mikrobiom jelitowy jest niezbędny do utrzymania dobrego zdrowia, podczas gdy nierównowaga, znana jako dysbioza, może prowadzić do różnych problemów zdrowotnych, w tym zaburzeń żołądkowo-jelitowych, otyłości i chorób autoimmunologicznych.
Research suggests that a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can promote a healthy microbiome.
Badania sugerują, że dieta bogata w błonnik, owoce, warzywa i produkty fermentowane może wspierać zdrowy mikrobiom.
Probiotics and prebiotics are also highlighted as beneficial for gut health, as they help support the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Probiotyki i prebiotyki są również podkreślane jako korzystne dla zdrowia jelit, ponieważ pomagają wspierać wzrost pożytecznych bakterii.
Recent studies are exploring the connection between the gut microbiome and other bodily systems, including the brain, indicating that gut health could influence mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Ostatnie badania badają związek między mikrobiomem jelitowym a innymi systemami ciała, w tym mózgiem, wskazując, że zdrowie jelit może wpływać na stany zdrowia psychicznego, takie jak lęki i depresja.
The understanding of the gut microbiome's importance has led to increased interest in personalized nutrition and therapies aimed at restoring microbial balance to improve overall health.
Zrozumienie znaczenia mikrobiomu jelitowego doprowadziło do zwiększenia zainteresowania spersonalizowaną dietą i terapiami mającymi na celu przywracanie równowagi mikrobiologicznej w celu poprawy ogólnego zdrowia.
